如何在 Python 列表中查找項目的索引
已發表: 2022-06-29在本指南中,您將學習如何使用簡單的迭代和內置的列表方法index()在 Python 列表中查找元素的索引。
使用 Python 列表時,您可能需要找出特定項目出現的索引。 您可以通過以下方式做到這一點:
- 遍歷列表並檢查當前索引處的項目是否等於特定值
- 使用內置列表方法
index()
您將在本教程中學習上述兩種方法。 讓我們開始吧。
Python 列表,重溫
在 Python 中,列表是相同或不同數據類型的項目的集合。 它們是可變的; 您可以就地修改它們,而無需創建新列表。
考慮這個例子fruits : 5 種不同水果的列表。
fruits = ["apple","mango","strawberry","pomegranate","melon"] 您可以使用內置的len()函數獲取任何 Python 對象的長度。 因此,您可以使用列表對象( fruits )作為參數調用len()函數來獲取其長度,如下所示。
len(fruits) # Output: 5 在本教程中,我們將使用fruits列表作為運行示例。
Python 列表中的索引
Python 遵循零索引。 所以在任何 Python 可迭代中,第一項在索引 0 處,第二項在索引 1 處,依此類推。 如果可迭代的長度為k ,則最後一項位於索引k - 1處。
在 Python 中,您可以使用 range() 函數在遍歷可迭代對象時獲取索引。
注意:當你遍歷
range(k)時,你會得到索引 0,1,2,…,(k-1)。 因此,通過設置k = len(list),您可以獲得所有有效索引的列表。
以下代碼單元對此進行了解釋。
for i in range(len(fruits)): print(f"i:{i}, fruit[{i}] is {fruits[i]}") # Output i:0, fruit[0] is apple i:1, fruit[1] is mango i:2, fruit[2] is strawberry i:3, fruit[3] is pomegranate i:4, fruit[4] is melon現在我們已經介紹了 Python 列表的基礎知識,讓我們學習如何在列表中查找項目的索引。

使用 for 循環通過迭代查找列表項的索引
讓我們考慮上一節中的fruits列表。 我們將學習如何使用for循環通過迭代來查找此列表中特定項目的索引。
使用 for 循環和 range() 函數
讓我們修復target :我們在列表中搜索的值。
您可以使用for循環和range()函數來獲取從0到len(fruits) - 1的索引列表。
- 遍歷訪問每個索引的水果列表。
- 檢查當前索引 i 處的項目是否等於目標。
- 如果為
True,則打印出已在索引i處找到target。
fruits = ["apple","mango","strawberry","pomegranate","melon"] target = "mango" for i in range(len(fruits)): if fruits[i] == target: print(f"{target} found at index {i}") # Output mango found at index 1 在此示例中,目標字符串'mango'在列表fruits中僅出現一次(在索引 1 處)。
但是,有時目標值出現不止一次或根本不出現。 為了處理這些情況,讓我們修改上面的循環並將內容包裝在一個名為find_in_list的函數中。
理解函數定義
函數find_in_list有兩個參數:
-
target:您要搜索的值,以及 py_list:您正在搜索的 Python 列表。
def find_in_list(target,py_list): target_indices = [] for i in range(len(fruits)): if fruits[i] == target: target_indices.append(i) if target_indices == []: print("Sorry, target not found!") else: print(f"{target} is found at indices {target_indices}") 在函數體中,我們初始化一個空列表target_indices 。 我們遍歷列表並訪問列表項。 如果在特定索引處找到目標,我們使用append()方法將該索引添加到target_indices列表中。
注意:在 Python 中,
list.append(item)將item添加到list的末尾。
- 如果永遠找不到目標,那麼
target_indices是一個空列表; 通知用戶目標不在列表中。 - 如果在多個索引處找到目標,則
target_indices包含所有這些索引。
接下來,讓我們重新定義fruits列表,如圖所示。
這次我們搜索target字符串'mango' ,它出現了兩次——在索引 1 和 4 處。
fruits = ["apple","mango","strawberry","pomegranate","mango","melon"] target = "mango" find_in_list(target,fruits) # Output mango is found at indices [1, 4] 在以target和fruits作為參數調用函數find_in_list時,我們看到兩個索引都返回了。
target = "turnip" find_in_list(target,fruits) # Output Sorry, target not found! 如果您嘗試搜索fruits列表中不存在的'turnip' ,您會收到一條消息,指出目標尚未找到。
使用 for 循環和 enumerate() 函數
在 Python 中,您可以使用enumerate()函數同時訪問索引和項目,而不必使用range()函數。
以下代碼單元顯示瞭如何使用enumerate()函數來獲取索引和項目。
fruits = ["apple","mango","strawberry","pomegranate","mango","melon"] for index,fruit in enumerate(fruits): print(f"Index {index}: {fruit}") # Output Index 0: apple Index 1: mango Index 2: strawberry Index 3: pomegranate Index 4: mango Index 5: melon 現在,讓我們重寫 Python 函數以使用enumerate()函數查找列表中項目的索引。

def find_in_list(target,py_list): target_indices = [] for index, fruit in enumerate(fruits): if fruit == target: target_indices.append(index) if target_indices == []: print("Sorry, target not found!") else: print(f"{target} is found at indices {target_indices}") 與上一節一樣,您現在可以使用有效參數調用find_in_list函數。
您可以將上述函數定義轉換為等效的列表推導式,我們將在下一節中這樣做。
使用列表理解通過迭代查找列表項的索引
Python 中的列表推導允許您根據某些條件從現有列表創建列表。 這是一般構造:
new_list = [<output> for <items in existing iterables> if <condition is true>] 下圖描述瞭如何識別列表理解的元素; 使用它,您可以將函數find_in_list轉換為列表理解。
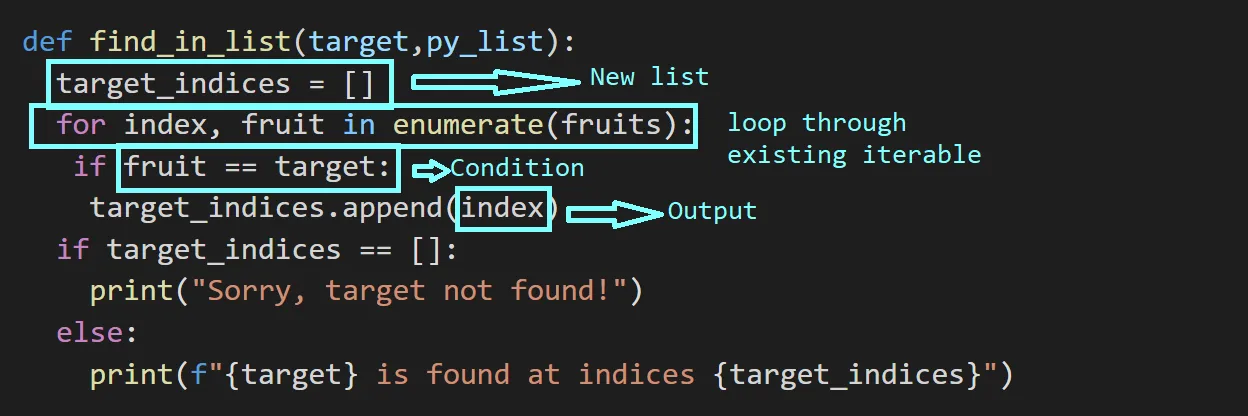
使用上述內容,用於創建目標索引的列表推導表達式如下。
target_indices = [index for index,fruit in enumerate(fruits) if fruit==target]作為練習,您可以嘗試運行上面的代碼片段以獲取其他一些示例。
使用 index() 方法查找列表項的索引
要在 Python 列表中查找項目的索引,您還可以使用內置的.index()方法。 這是一般語法:
list.index(value,start,end)解析上述方法:
-
value是您要搜索的目標值。 -
start和end是可選的位置參數; 您可以使用它們在列表切片中搜索從start並一直延伸到end - 1的項目的索引。
注意: .index()方法僅返回
list中第一次出現value的索引。 即使您在列表切片[start: end-1]中找到項目的索引,此方法也僅返回與該項目的第一次出現相對應的索引。
讓我們重新審視我們的示例以了解.index()方法的工作原理。
fruits = ["apple","mango","strawberry","pomegranate","mango","melon"] target = "mango" fruits.index(target) 1 即使fruits列表中出現了兩次'mango' ,您也可以看到只返回了第一次出現的索引。
要獲得第二次出現的芒果的索引,我們可以搜索從索引 2 開始並一直延伸到索引 5 的列表切片,如下所示。
fruits.index(target,2,5) 4如何在 Python 中處理 ValueErrors
現在讓我們看看如果您嘗試查找列表中不存在的項目的索引會發生什麼,例如'carrot' 。
target = "carrot" fruits.index(target) # Output --------------------------------------------------------------------------- ValueError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-17-81bd454e44f7> in <module>() 1 target = "carrot" 2 ----> 3 fruits.index(target) ValueError: 'carrot' is not in list 如上面的代碼單元所示,這會引發 ValueError。 在 Python 中,您可以使用try和except塊將其作為異常處理。
使用try-except的一般語法如下。
try: # to do this except <ErrorType>: # do this to handle <ErrorType> as exception使用上面的 try-except 塊,我們可以將ValueError作為異常處理。
target = "carrot" try: fruits.index(target) except ValueError: print(f"Sorry, could not find {target} in list") # Output Sorry, could not find carrot in list上面的代碼執行以下操作:
- 如果目標存在於列表中,則返回目標的索引。
- 如果目標不存在,它將ValueError作為異常處理並打印出錯誤消息。
加起來
這裡總結了你已經學會的在 Python 列表中查找項目索引的不同方法。
- 您可以使用 Python 的for循環和range()函數來獲取項目及其各自的索引。 檢查索引處的項目是否與目標匹配。
- 您還可以使用enumerate()函數同時訪問項目和索引。
- 您可以在列表推導表達式中使用上述兩種方法。
- 要在列表中查找項目的索引,您還可以使用內置的.index()方法。
- list.index(value)返回list中第一次出現value的索引。 如果該值不存在,則會引發ValueError 。
- 您可以使用list.index(value, start, end)搜索列表的某個切片,以搜索列表切片[start:end-1]中出現的值。
接下來,學習按鍵或按值對 Python 字典進行排序。 快樂的 Python 編程!
