Google 지도의 Android 자습서: 두 점 사이의 경로 그리기
게시 됨: 2018-05-30이 게시물에서는 Google 지도에서 두 지점 사이의 경로를 그리는 방법에 대해 설명합니다.
먼저 앱에 Google 지도 통합이 필요합니다. 이렇게 하려면 다음을 방문하십시오.
- https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/android-api/signup
- 키 받기 버튼 클릭
아래와 유사한 대화 상자가 표시됩니다.
새 프로젝트를 만들고 다음을 클릭합니다. 아래와 같은 API 키가 제공됩니다.
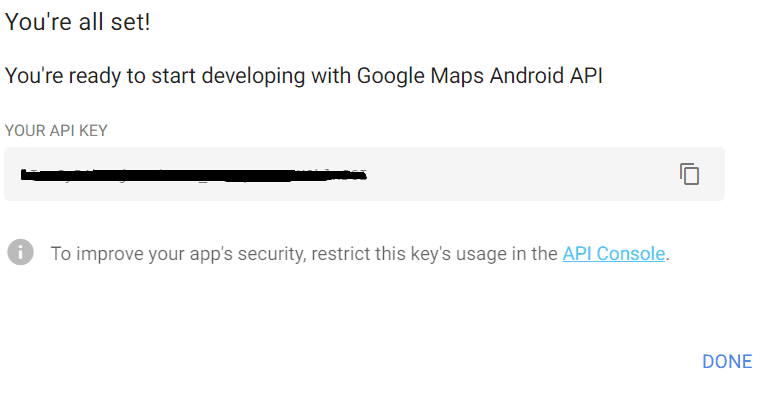
이 키 사용을 제한하기로 선택한 경우 API 콘솔을 클릭한다고 가정합니다. 그렇지 않으면 완료를 클릭합니다.
API 콘솔에서 웹사이트, Android 앱, IOS 앱 등에 대해서만 키 사용을 제한할 수 있습니다.
API 콘솔을 클릭하면 생성 날짜, 만든 사람 등이 있는 다른 페이지로 리디렉션됩니다. 제한해야 하는 API 키를 선택한 다음 Android 앱 라디오 버튼을 클릭합니다.
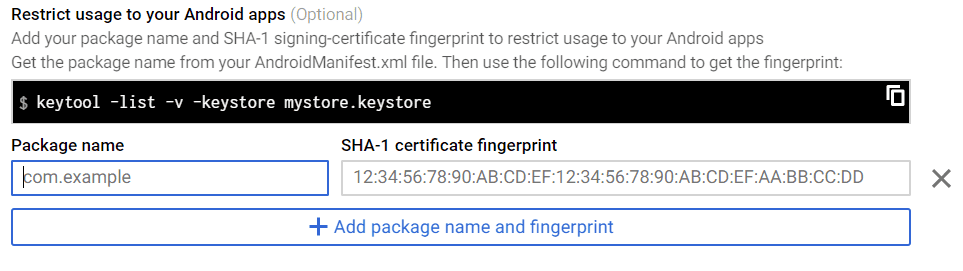
Android 앱에 대한 사용을 제한하고 패키지 이름과 지문을 추가한다고 가정합니다.
Androidmanifest.xml 파일에서 패키지 이름을 가져올 수 있습니다.
지문을 추가하려면 SHA-1 인증서를 받아야 합니다. 이를 위해 Android Studio를 방문하여 오른쪽 모서리에 있는 Gradle 파일을 엽니다.
또한 앱 gradle >> 작업 >> android >> 서명 보고서를 클릭하십시오.
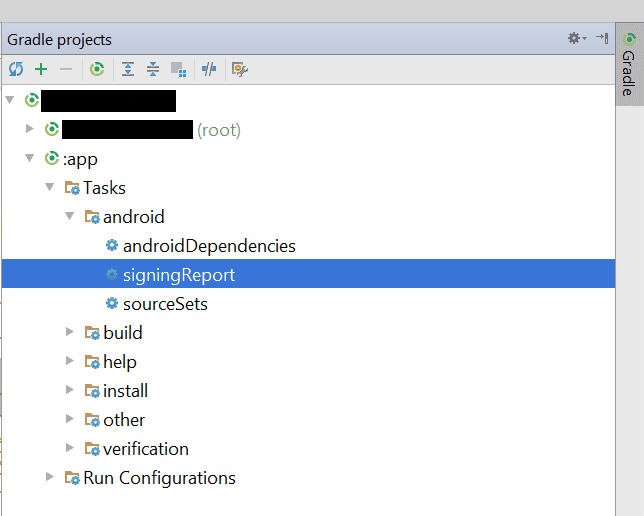
SHA-1 인증서를 복사하여 위 이미지와 같이 SHA-1 지문 상자에 붙여넣습니다. 마지막으로 SAVE 버튼을 클릭합니다.
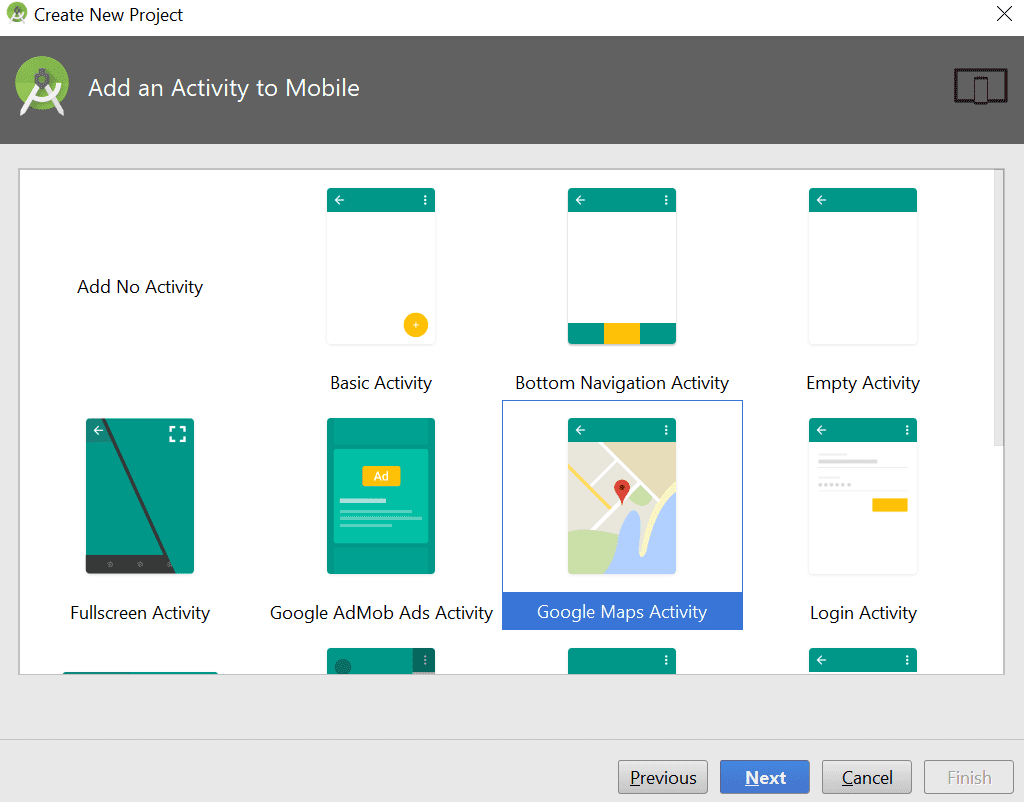
이제 이름, 회사 도메인 및 기타 세부 정보를 사용하여 새 Android 프로젝트를 만듭니다. Android 버전을 Lollipop으로 선택하고 아래와 같이 Google Map Activity에서 경로 그리기를 선택합니다. 이제 다음을 클릭하고 완료 버튼을 클릭합니다.
프로젝트를 생성한 후 다음과 같은 파일을 볼 수 있습니다.
- MapsActivity.java
- Activity_maps.xml
- google_maps-api.xml
먼저 google_map_api.xml을 변경합니다 . 이 파일에 이전에 생성한 Google API 키를 추가합니다.
<string name="google_maps_key" templateMergeStrategy="preserve" translatable="false">API Key</string>다음으로 Androidmanifest.xml 파일을 변경합니다.
- 인터넷 연결 - api와 통신하고 위치를 얻으려면
- READ_GSERVICES - 앱이 Google 서비스 프레임워크를 사용하려고 할 때마다
- ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION - Wi-Fi 및 모바일 데이터를 사용하여 사용자 위치를 결정합니다. 대략적인 위치를 알려줍니다
- ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION- GPS를 사용하여 사용자 위치를 결정합니다. 정확한 위치를 알려드립니다.
- 또한 API 키 값이 포함된 애플리케이션 태그에 메타데이터 태그를 추가합니다.
Androidmanifest.xml 파일은 아래와 같습니다.
<manifest xmlns:andro package="com.example.drawroutes"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="com.google.android.providers.gsf.permission.READ_GSERVICES" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="@string/google_maps_key" /> <activity android:name=".MapsActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>이제 build.gradle 파일에서 변경하십시오. 변경하는 동안 다음과 같은 두 가지 종속성을 추가해야 합니다.
- 구현 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:11.8.0'
- 구현 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-location:11.8.0'
첫 번째 종속성은 Google 지도를 표시하는 데 사용되지만 두 번째 종속성은 Google 위치 및 활동 인식을 가져오는 데 사용됩니다.
따라서 build.gradle 파일은 다음과 같습니다.
apply plugin: 'com.android.application' android { compileSdkVersion 26 defaultConfig { applicationId "com.example.drawroutes" minSdkVersion 19 targetSdkVersion 26 versionCode 1 versionName "1.0" testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" } buildTypes { release { minifyEnabled false proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro' } } } dependencies { implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar']) implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0' implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:11.8.0' implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-location:11.8.0' }MapsActivity부터 시작하겠습니다. 이 활동에서 Activity_maps라는 레이아웃 파일을 설정합니다.
이 xml 파일에서 프래그먼트를 정의하고 프래그먼트의 ID와 이름을 선언합니다. 마지막으로 xml은 아래와 같습니다 .
<fragment xmlns:andro xmlns:tools="schemas.android.com/tools" android: android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.drawroutes.MapsActivity" />FragmentActivity에서 활동을 확장하기 때문에 여기에서 android: name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment"를 선언하고 있습니다. MapFragment를 사용하려면 Activity를 확장할 수 있습니다.
다음으로 id가 다음과 같이 정의된 MapsActivity를 확장합니다.
Final SupportMapFragment mapFragment =(SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map);여기에서 코드를 나누어 차례로 논의해 보겠습니다. 먼저 GoogleMap 클래스를 인스턴스화해야 합니다.
이제 지도를 onClick 리스너 선언
mMap.setOnMapClickListener(new GoogleMap.OnMapClickListener() { @Override public void onMapClick(LatLng point) { // Already two locations if (MarkerPoints.size() > 1) { MarkerPoints.clear(); mMap.clear(); } // Adding new item to the ArrayList MarkerPoints.add(point); // Creating MarkerOptions MarkerOptions options = new MarkerOptions(); // Setting the position of the marker options.position(point); /** * For the start location, the color of marker is GREEN and * for the end location, the color of marker is RED. */ if (MarkerPoints.size() == 1) { options.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.defaultMarker(BitmapDescriptorFactory.HUE_GREEN)); } else if (MarkerPoints.size() == 2) { options.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.defaultMarker(BitmapDescriptorFactory.HUE_RED)); } // Add new marker to the Google Map Android API V2 mMap.addMarker(options); // Checks, whether start and end locations are captured if (MarkerPoints.size() >= 2) { LatLng origin = MarkerPoints.get(0); LatLng dest = MarkerPoints.get(1); // Getting URL to the Google Directions API String url = getUrl(origin, dest); Log.d("onMapClick", url.toString()); FetchUrl FetchUrl = new FetchUrl(); // Start downloading json data from Google Directions API FetchUrl.execute(url); //move map camera mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(origin)); mMap.animateCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.zoomTo(11)); } } });위의 코드는 사용자가 Android 화면을 탭할 때 실행됩니다. 이것은 경로가 그려질 지점에 마커를 배치하는 데 사용됩니다.
MarkerPoints.get() 은 두 점의 좌표에 액세스하고 저장하는 데 사용됩니다. LatLng 출발지와 목적지에 저장됩니다.
그리고 getUrl 은 URL을 가져오는 데 사용되며 Async Task를 사용하여 구현됩니다.
Async Task: Async Task는 Android에서 제공하는 Abstract 클래스로 UI 스레드를 사용하는 데 도움이 됩니다. Async Task 클래스를 사용하면 장기 실행 작업이나 백그라운드 작업을 수행하고 메인 스레드에 영향을 주지 않고 UI 스레드에 결과를 표시할 수 있습니다. 비동기 작업은 백그라운드에서 비동기적으로 수행해야 하는 작업/작업을 실행하는 데 사용됩니다. Async Task 클래스에는 두 가지 메서드가 있습니다.
- doInbackground : 이 메소드에서 작업이 구현됩니다.
- onPostExecute: 이 메소드에 결과가 표시됩니다.
private class FetchUrl extends AsyncTask<String, Void, String> { @Override protected String doInBackground(String... url) { // For storing data from web service String data = ""; try { // Fetching the data from web service data = downloadUrl(url[0]); Log.d("Background Task data", data.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { Log.d("Background Task", e.toString()); } return data; } @Override protected void onPostExecute(String result) { super.onPostExecute(result); ParserTask parserTask = new ParserTask(); // Invokes the thread for parsing the JSON data parserTask.execute(result); } }downloadUrl: 웹 서비스에서 URL을 가져오는 데 사용되며 그 결과는 ParserTask를 사용하여 구문 분석됩니다. 이것은 또한 비동기 작업입니다.

private String downloadUrl(String strUrl) throws IOException { String data = ""; InputStream iStream = null; HttpURLConnection urlConnection = null; try { URL url = new URL(strUrl); // Creating an http connection to communicate with url urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // Connecting to url urlConnection.connect(); // Reading data from url iStream = urlConnection.getInputStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(iStream)); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); String line = ""; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { sb.append(line); } data = sb.toString(); Log.d("downloadUrl", data.toString()); br.close(); } catch (Exception e) { Log.d("Exception", e.toString()); } finally { iStream.close(); urlConnection.disconnect(); } return data; }여기서 데이터는 Json 형식으로 반환됩니다. HttpURLConnection을 사용하여 얻을 수 있는 사용자.
Parser Task: AsyncTask를 확장하는 ParserTask라는 이름으로 새 클래스를 정의합니다. downloadUrl 메서드에서 반환된 Json 데이터를 구문 분석합니다.
private class ParserTask extends AsyncTask<String, Integer, List<List<HashMap<String, String>>>> { // Parsing the data in non-ui thread @Override protected List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> doInBackground(String... jsonData) { JSONObject jObject; List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> routes = null; try { jObject = new JSONObject(jsonData[0]); Log.d("ParserTask",jsonData[0].toString()); DataParser parser = new DataParser(); Log.d("ParserTask", parser.toString()); // Starts parsing data routes = parser.parse(jObject); Log.d("ParserTask","Executing routes"); Log.d("ParserTask",routes.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { Log.d("ParserTask",e.toString()); e.printStackTrace(); } return routes; } // Executes in UI thread, after the parsing process @Override protected void onPostExecute(List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> result) { ArrayList<LatLng> points; PolylineOptions lineOptions = null; // Traversing through all the routes for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) { points = new ArrayList<>(); lineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); // Fetching i-th route List<HashMap<String, String>> path = result.get(i); // Fetching all the points in i-th route for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) { HashMap<String, String> point = path.get(j); double lat = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lat")); double lng = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lng")); LatLng position = new LatLng(lat, lng); points.add(position); } // Adding all the points in the route to LineOptions lineOptions.addAll(points); lineOptions.width(10); lineOptions.color(Color.RED); Log.d("onPostExecute","onPostExecute lineoptions decoded"); } // Drawing polyline in the Google Map for the i-th route if(lineOptions != null) { mMap.addPolyline(lineOptions); } else { Log.d("onPostExecute","without Polylines drawn"); } } }여기서 "doInBackround"는 데이터를 구문 분석합니다. "onPostExecute" 메소드에서 폴리라인을 추가하여 Google 지도에 경로를 그립니다.
이러한 방법을 따르면 데이터를 다른 클래스(예: DataParser)로 구문 분석합니다.
class DataParser { List<List<HashMap<String,String>>> parse(JSONObject jObject){ List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> routes = new ArrayList<>() ; JSONArray jRoutes; JSONArray jLegs; JSONArray jSteps; try { jRoutes = jObject.getJSONArray("routes"); /** Traversing all routes */ for(int i=0;i<jRoutes.length();i++){ jLegs = ( (JSONObject)jRoutes.get(i)).getJSONArray("legs"); List path = new ArrayList<>(); /** Traversing all legs */ for(int j=0;j<jLegs.length();j++){ jSteps = ( (JSONObject)jLegs.get(j)).getJSONArray("steps"); /** Traversing all steps */ for(int k=0;k<jSteps.length();k++){ String polyline = ""; polyline = (String)((JSONObject)((JSONObject)jSteps.get(k)).get("polyline")).get("points"); List<LatLng> list = decodePoly(polyline); /** Traversing all points */ for(int l=0;l<list.size();l++){ HashMap<String, String> hm = new HashMap<>(); hm.put("lat", Double.toString((list.get(l)).latitude) ); hm.put("lng", Double.toString((list.get(l)).longitude) ); path.add(hm); } } routes.add(path); } } } catch (JSONException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ } return routes; } /** * Method to decode polyline points * */ private List<LatLng> decodePoly(String encoded) { List<LatLng> poly = new ArrayList<>(); int index = 0, len = encoded.length(); int lat = 0, lng = 0; while (index < len) { int b, shift = 0, result = 0; do { b = encoded.charAt(index++) - 63; result |= (b & 0x1f) << shift; shift += 5; } while (b >= 0x20); int dlat = ((result & 1) != 0 ? ~(result >> 1) : (result >> 1)); lat += dlat; shift = 0; result = 0; do { b = encoded.charAt(index++) - 63; result |= (b & 0x1f) << shift; shift += 5; } while (b >= 0x20); int dlng = ((result & 1) != 0 ? ~(result >> 1) : (result >> 1)); lng += dlng; LatLng p = new LatLng((((double) lat / 1E5)), (((double) lng / 1E5))); poly.add(p); } return poly; } }parse 메소드를 사용하면 getJSONArray를 사용하여 JSONArray를 분할할 수 있는 Json 데이터를 얻을 수 있습니다. 모든 경로, 점 등을 순회하고 모든 순회 점을 목록에 추가합니다.
route.add(경로);
폴리라인을 사용하여 Google 지도에 경로를 그립니다. 이는 ParseTask AsyncTask 클래스가 있는 onPostExecute 메서드에서 수행됩니다.
@Override protected void onPostExecute(List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> result) { ArrayList<LatLng> points; PolylineOptions lineOptions = null; // Traversing through all the routes for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) { points = new ArrayList<>(); lineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); // Fetching i-th route List<HashMap<String, String>> path = result.get(i); // Fetching all the points in i-th route for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) { HashMap<String, String> point = path.get(j); double lat = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lat")); double lng = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lng")); LatLng position = new LatLng(lat, lng); points.add(position); } // Adding all the points in the route to LineOptions lineOptions.addAll(points); lineOptions.width(10); lineOptions.color(Color.RED); Log.d("onPostExecute","onPostExecute lineoptions decoded"); } // Drawing polyline in the Google Map for the i-th route if(lineOptions != null) { mMap.addPolyline(lineOptions); } else { Log.d("onPostExecute","without Polylines drawn"); } }결과에서 위의 점들을 가져와서 구글 지도에 경로를 그립니다. 여기서 ArrayList 포인트는 Google 지도에 위도 및 경도 위치를 저장하는 데 사용됩니다.
마지막으로 polyLine을 사용하여 Google Map에 경로를 그립니다. lineOptions.addAll(points);
다음과 같이 지도에 폴리라인을 추가합니다. mMap.addPolyline(lineOptions);
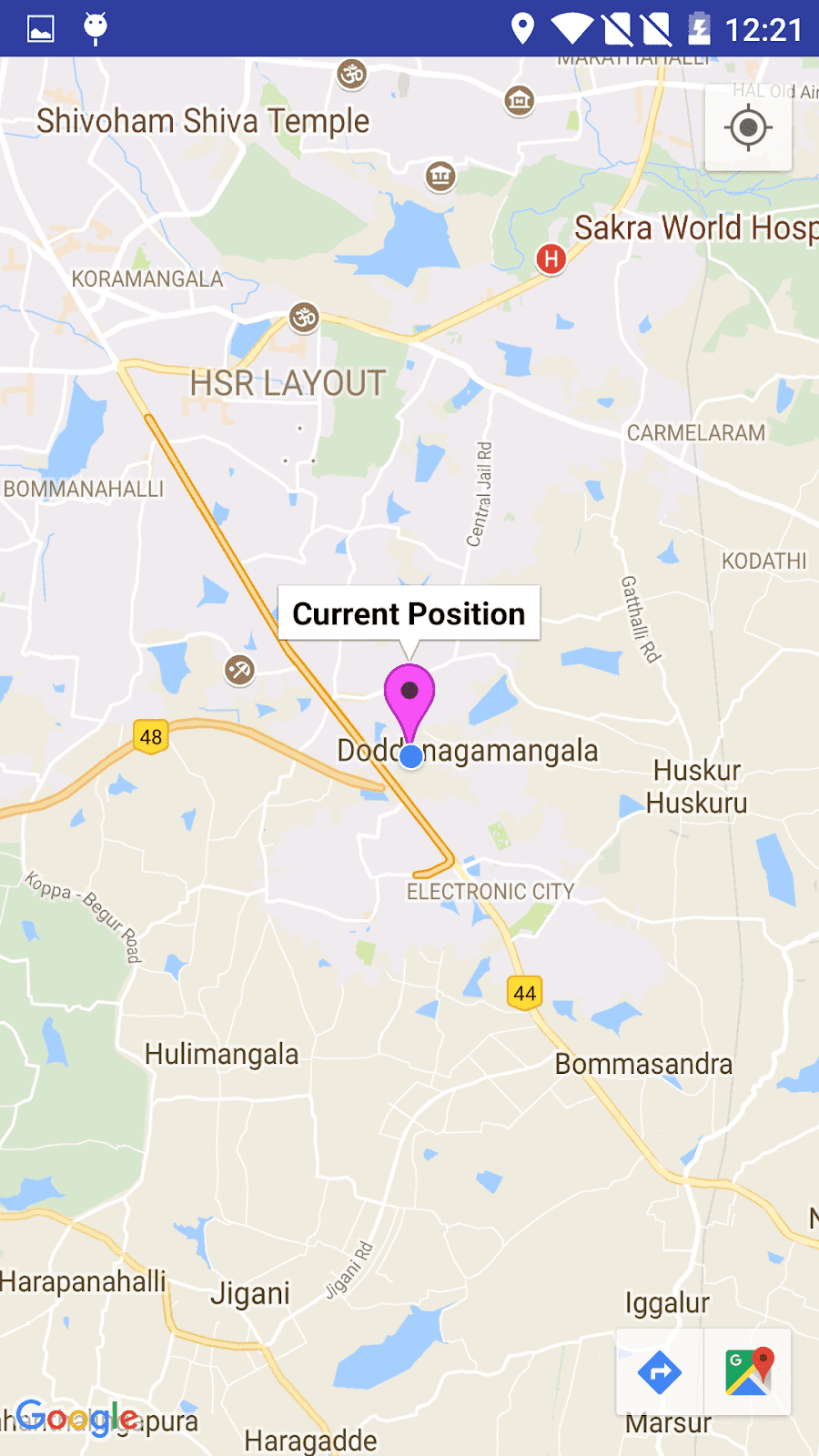
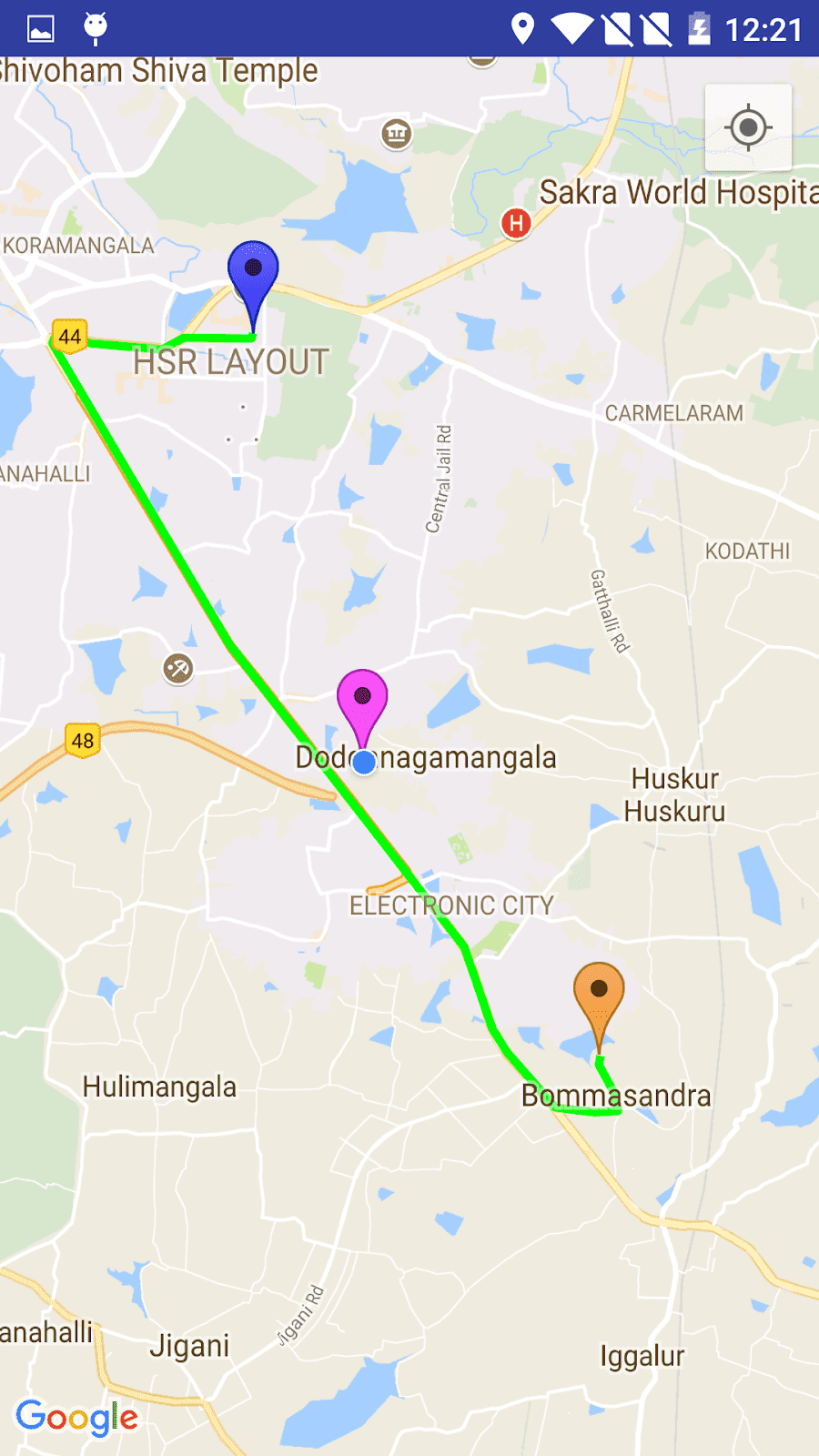
마지막으로 애플리케이션을 실행합니다. 성공적으로 실행됩니다. 화면 출력은 아래와 같습니다.