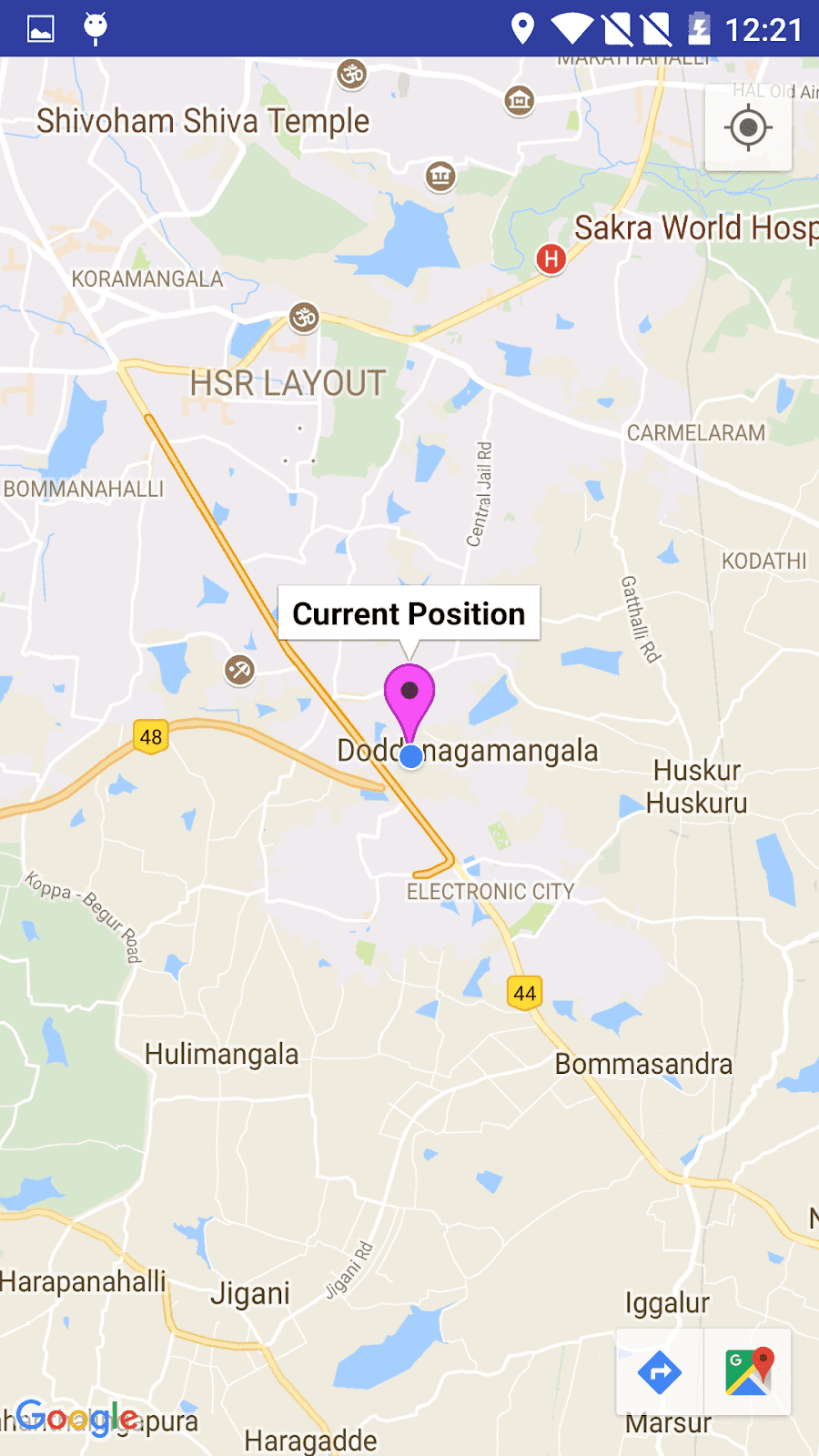
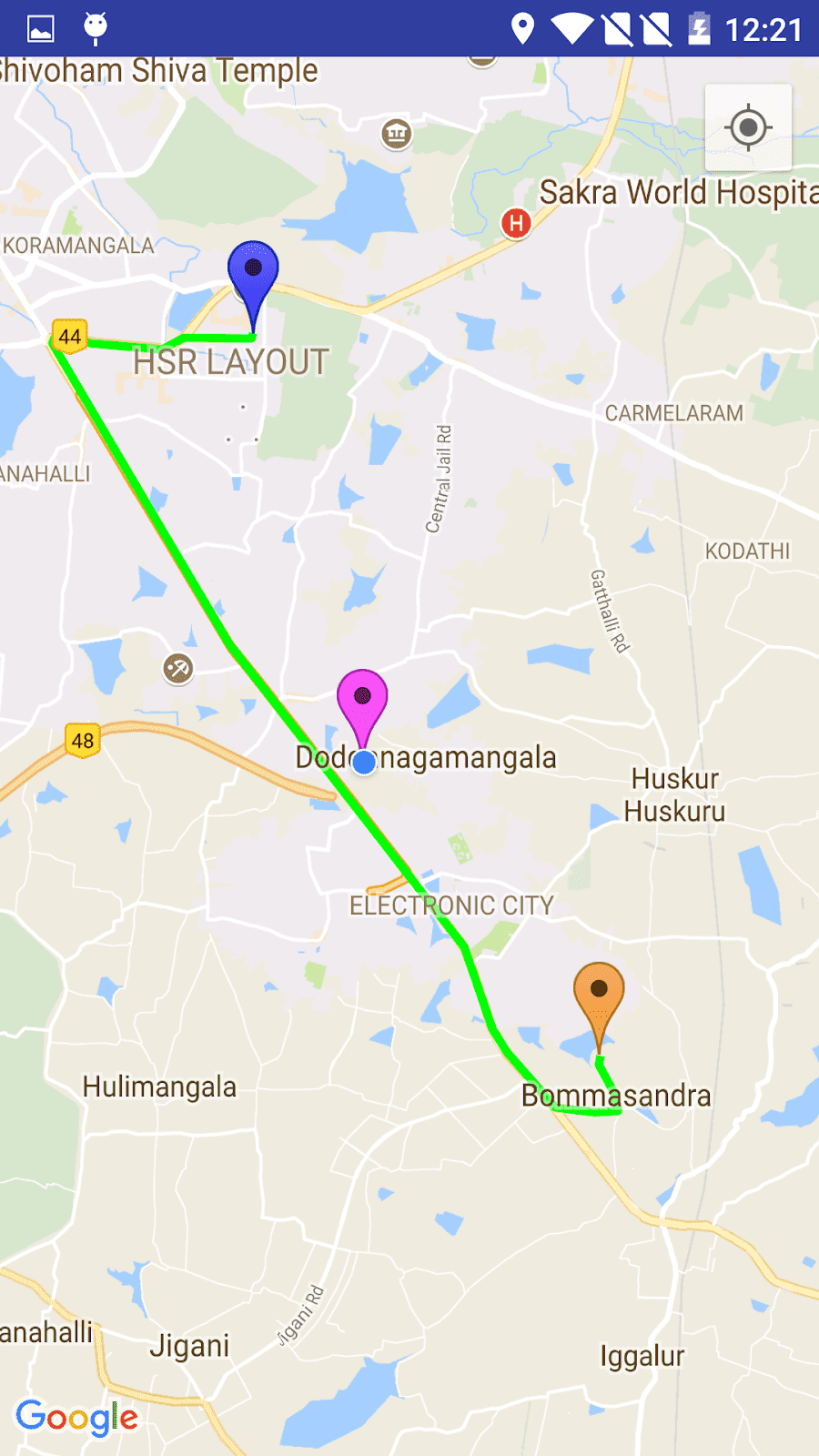
谷歌地圖上的安卓教程:繪製兩點之間的路線
已發表: 2018-05-30在這篇文章中,我們將討論如何在谷歌地圖上繪製兩點之間的路線。
首先,我們需要在我們的應用程序上集成 Google 地圖。 為此,請訪問
- https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/android-api/signup
- 單擊“獲取密鑰”按鈕
您將看到一個類似於下面的對話框。
創建一個新項目並單擊下一步。 您將看到如下所示的 API 密鑰。
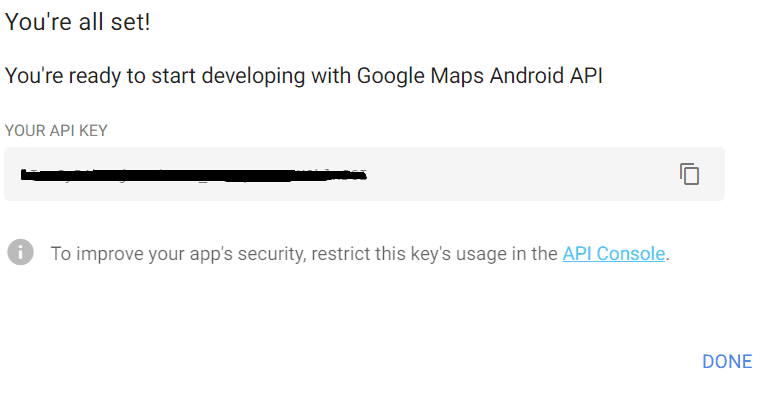
假設,如果您選擇限制此密鑰的使用,請單擊 API 控制台。 否則,單擊完成。
在 API 控制台中,您可以僅限製網站、Android 應用程序、IOS 應用程序等的密鑰使用。
單擊 API 控制台後,您將被重定向到另一個頁面,其中包含創建日期、創建者等。選擇應限制的 API 密鑰,然後單擊 Android 應用程序單選按鈕。
假設您想限制對您的 android 應用程序的使用,添加包名稱和指紋。
您可以從Androidmanifest.xml文件中獲取包名稱。
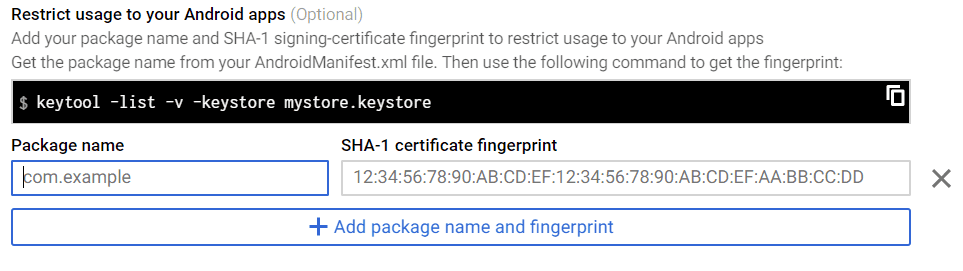
要添加指紋,您必須獲得 SHA-1 證書。 為此,請訪問 Android Studio 並打開右上角的 Gradle 文件。
進一步,點擊 App gradle >> Tasks >> android >>signingreport
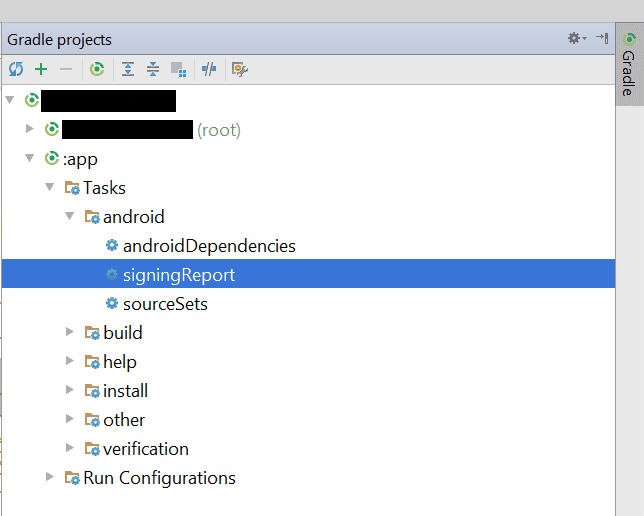
複製 SHA-1 證書並將其粘貼到 SHA-1 指紋框中,如上圖所示。 最後,單擊“保存”按鈕。
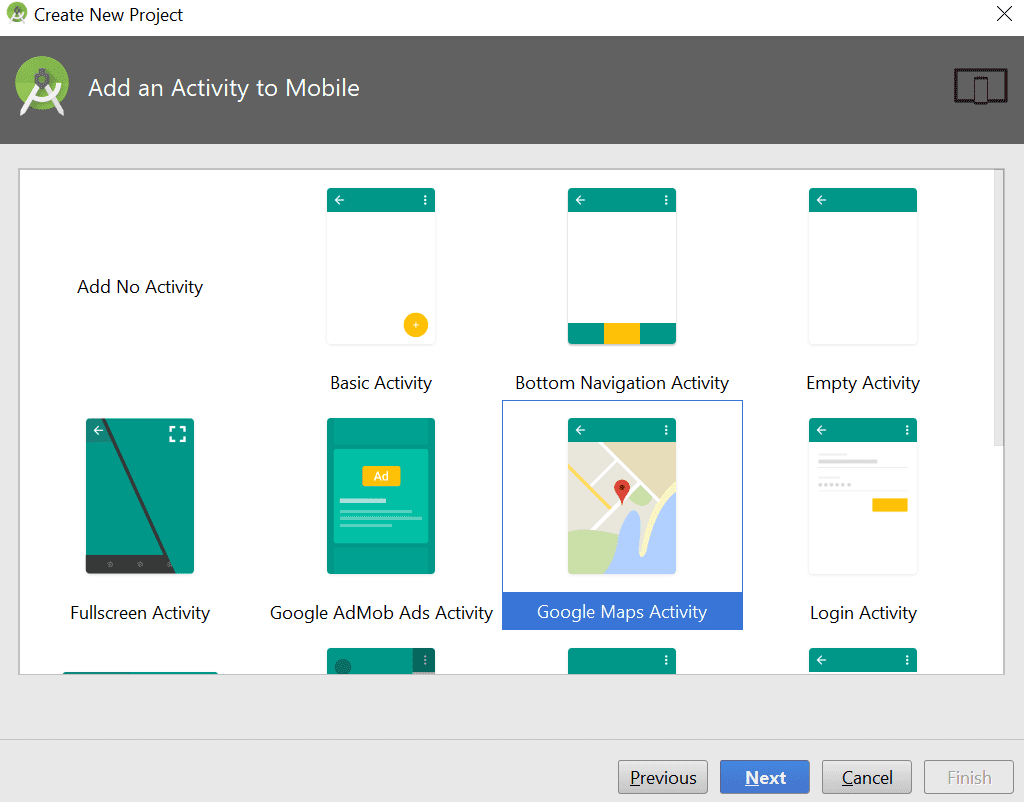
現在使用名稱、公司域和其他詳細信息創建一個新的 Android 項目。 選擇你的安卓版本為棒棒糖,然後在谷歌地圖活動中選擇如下圖所示的繪製路線。 現在單擊下一步並完成按鈕。
創建項目後,您可以看到一些文件,例如
- 地圖活動.java
- Activity_maps.xml
- google_maps-api.xml
首先,更改google_map_api.xml。 在此文件中,添加我們之前創建的 Google API 密鑰。
<string name="google_maps_key" templateMergeStrategy="preserve" translatable="false">API Key</string>接下來,更改 Androidmanifest.xml 文件
- Internet 連接 - 與 api 通信並獲取位置
- READ_GSERVICES - 每當應用程序想要使用 Google 服務框架時
- ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION - 它將使用 Wifi 和移動數據確定用戶位置。 它將給出大概的位置
- ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION- 它將使用 GPS 確定用戶位置。 它會給你準確的位置。
- 此外,在包含 API 密鑰值的應用程序標籤中添加元數據標籤
Androidmanifest.xml 文件如下所示
<manifest xmlns:andro package="com.example.drawroutes"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="com.google.android.providers.gsf.permission.READ_GSERVICES" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY" android:value="@string/google_maps_key" /> <activity android:name=".MapsActivity" android:label="@string/title_activity_maps"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>現在更改 build.gradle 文件。 更改時,請確保添加兩個依賴項,它們是:
- 實現 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:11.8.0'
- 實現 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-location:11.8.0'
第一個依賴項用於顯示谷歌地圖,第二個依賴項用於獲取谷歌位置和活動識別。
所以 build.gradle 文件如下所示
apply plugin: 'com.android.application' android { compileSdkVersion 26 defaultConfig { applicationId "com.example.drawroutes" minSdkVersion 19 targetSdkVersion 26 versionCode 1 versionName "1.0" testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" } buildTypes { release { minifyEnabled false proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro' } } } dependencies { implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar']) implementation 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:26.1.0' implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-maps:11.8.0' implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-location:11.8.0' }讓我們從 MapsActivity 開始。 在此活動中,我們設置名為 Activity_maps 的佈局文件
在這個 xml 文件中定義一個 Fragment,並聲明該 Fragment 的 id 和 name。 最後xml如下所示。
<fragment xmlns:andro xmlns:tools="schemas.android.com/tools" android: android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.drawroutes.MapsActivity" />您在這裡聲明android: name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment"因為我們是從 FragmentActivity 擴展活動。 如果你想使用 MapFragment 那麼你可以擴展 Activity。
接下來,擴展 MapsActivity,其中 id 以這種方式定義:
Final SupportMapFragment mapFragment =(SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map);讓我們在這里分一下代碼,一個接一個地討論。 首先,您需要實例化 GoogleMap 類。
現在聲明地圖 onClick Listner
mMap.setOnMapClickListener(new GoogleMap.OnMapClickListener() { @Override public void onMapClick(LatLng point) { // Already two locations if (MarkerPoints.size() > 1) { MarkerPoints.clear(); mMap.clear(); } // Adding new item to the ArrayList MarkerPoints.add(point); // Creating MarkerOptions MarkerOptions options = new MarkerOptions(); // Setting the position of the marker options.position(point); /** * For the start location, the color of marker is GREEN and * for the end location, the color of marker is RED. */ if (MarkerPoints.size() == 1) { options.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.defaultMarker(BitmapDescriptorFactory.HUE_GREEN)); } else if (MarkerPoints.size() == 2) { options.icon(BitmapDescriptorFactory.defaultMarker(BitmapDescriptorFactory.HUE_RED)); } // Add new marker to the Google Map Android API V2 mMap.addMarker(options); // Checks, whether start and end locations are captured if (MarkerPoints.size() >= 2) { LatLng origin = MarkerPoints.get(0); LatLng dest = MarkerPoints.get(1); // Getting URL to the Google Directions API String url = getUrl(origin, dest); Log.d("onMapClick", url.toString()); FetchUrl FetchUrl = new FetchUrl(); // Start downloading json data from Google Directions API FetchUrl.execute(url); //move map camera mMap.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLng(origin)); mMap.animateCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.zoomTo(11)); } } });當用戶點擊 Android 屏幕時,將執行上面顯示的代碼。 這用於將標記放置在將繪製路徑之間的點上。
MarkerPoints.get()用於訪問和存儲兩個點的坐標。 它將存儲在 LatLng 起點和目的地。
getUrl用於獲取 URL 並使用 Async Task 實現。
Async Task: Async Task是Android提供的一個抽像類,有助於使用UI線程。 Async Task 類允許我們執行長時間運行的操作或後台操作,並在不影響主線程的情況下在 UI 線程上顯示結果。 Async Task 用於運行需要在後台異步執行的任務/操作。 在 Async Task 類中有兩種方法。
- doInbackground :任務將在此方法中實現。
- onPostExecute:結果將顯示在此方法中。
private class FetchUrl extends AsyncTask<String, Void, String> { @Override protected String doInBackground(String... url) { // For storing data from web service String data = ""; try { // Fetching the data from web service data = downloadUrl(url[0]); Log.d("Background Task data", data.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { Log.d("Background Task", e.toString()); } return data; } @Override protected void onPostExecute(String result) { super.onPostExecute(result); ParserTask parserTask = new ParserTask(); // Invokes the thread for parsing the JSON data parserTask.execute(result); } }downloadUrl:用於從 Web 服務獲取 URL,其結果將使用 ParserTask 進行解析。 這也是一個異步任務。

private String downloadUrl(String strUrl) throws IOException { String data = ""; InputStream iStream = null; HttpURLConnection urlConnection = null; try { URL url = new URL(strUrl); // Creating an http connection to communicate with url urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // Connecting to url urlConnection.connect(); // Reading data from url iStream = urlConnection.getInputStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(iStream)); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); String line = ""; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { sb.append(line); } data = sb.toString(); Log.d("downloadUrl", data.toString()); br.close(); } catch (Exception e) { Log.d("Exception", e.toString()); } finally { iStream.close(); urlConnection.disconnect(); } return data; }這里數據會以Json的形式返回。 哪個用戶可以使用 HttpURLConnection 獲得。
Parser Task:定義名為 ParserTask 的新類,它擴展了 AsyncTask。 解析downloadUrl方法返回的Json數據。
private class ParserTask extends AsyncTask<String, Integer, List<List<HashMap<String, String>>>> { // Parsing the data in non-ui thread @Override protected List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> doInBackground(String... jsonData) { JSONObject jObject; List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> routes = null; try { jObject = new JSONObject(jsonData[0]); Log.d("ParserTask",jsonData[0].toString()); DataParser parser = new DataParser(); Log.d("ParserTask", parser.toString()); // Starts parsing data routes = parser.parse(jObject); Log.d("ParserTask","Executing routes"); Log.d("ParserTask",routes.toString()); } catch (Exception e) { Log.d("ParserTask",e.toString()); e.printStackTrace(); } return routes; } // Executes in UI thread, after the parsing process @Override protected void onPostExecute(List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> result) { ArrayList<LatLng> points; PolylineOptions lineOptions = null; // Traversing through all the routes for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) { points = new ArrayList<>(); lineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); // Fetching i-th route List<HashMap<String, String>> path = result.get(i); // Fetching all the points in i-th route for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) { HashMap<String, String> point = path.get(j); double lat = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lat")); double lng = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lng")); LatLng position = new LatLng(lat, lng); points.add(position); } // Adding all the points in the route to LineOptions lineOptions.addAll(points); lineOptions.width(10); lineOptions.color(Color.RED); Log.d("onPostExecute","onPostExecute lineoptions decoded"); } // Drawing polyline in the Google Map for the i-th route if(lineOptions != null) { mMap.addPolyline(lineOptions); } else { Log.d("onPostExecute","without Polylines drawn"); } } }在這裡,“doInBackround”將解析數據。 在“onPostExecute”方法中,我們將添加折線以在谷歌地圖上繪製路線。
通過遵循這些方法,我們將數據解析到另一個類,即 DataParser
class DataParser { List<List<HashMap<String,String>>> parse(JSONObject jObject){ List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> routes = new ArrayList<>() ; JSONArray jRoutes; JSONArray jLegs; JSONArray jSteps; try { jRoutes = jObject.getJSONArray("routes"); /** Traversing all routes */ for(int i=0;i<jRoutes.length();i++){ jLegs = ( (JSONObject)jRoutes.get(i)).getJSONArray("legs"); List path = new ArrayList<>(); /** Traversing all legs */ for(int j=0;j<jLegs.length();j++){ jSteps = ( (JSONObject)jLegs.get(j)).getJSONArray("steps"); /** Traversing all steps */ for(int k=0;k<jSteps.length();k++){ String polyline = ""; polyline = (String)((JSONObject)((JSONObject)jSteps.get(k)).get("polyline")).get("points"); List<LatLng> list = decodePoly(polyline); /** Traversing all points */ for(int l=0;l<list.size();l++){ HashMap<String, String> hm = new HashMap<>(); hm.put("lat", Double.toString((list.get(l)).latitude) ); hm.put("lng", Double.toString((list.get(l)).longitude) ); path.add(hm); } } routes.add(path); } } } catch (JSONException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (Exception e){ } return routes; } /** * Method to decode polyline points * */ private List<LatLng> decodePoly(String encoded) { List<LatLng> poly = new ArrayList<>(); int index = 0, len = encoded.length(); int lat = 0, lng = 0; while (index < len) { int b, shift = 0, result = 0; do { b = encoded.charAt(index++) - 63; result |= (b & 0x1f) << shift; shift += 5; } while (b >= 0x20); int dlat = ((result & 1) != 0 ? ~(result >> 1) : (result >> 1)); lat += dlat; shift = 0; result = 0; do { b = encoded.charAt(index++) - 63; result |= (b & 0x1f) << shift; shift += 5; } while (b >= 0x20); int dlng = ((result & 1) != 0 ? ~(result >> 1) : (result >> 1)); lng += dlng; LatLng p = new LatLng((((double) lat / 1E5)), (((double) lng / 1E5))); poly.add(p); } return poly; } }使用 parse 方法,您可以獲得可以使用 getJSONArray 拆分 JSONArray 的 Json 數據。 遍歷所有路線、點等並將所有遍歷點添加到列表中。
路線。添加(路徑);
使用折線在谷歌地圖上繪製路線。 這是在 ParseTask AsyncTask 類中的 onPostExecute 方法中完成的。
@Override protected void onPostExecute(List<List<HashMap<String, String>>> result) { ArrayList<LatLng> points; PolylineOptions lineOptions = null; // Traversing through all the routes for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) { points = new ArrayList<>(); lineOptions = new PolylineOptions(); // Fetching i-th route List<HashMap<String, String>> path = result.get(i); // Fetching all the points in i-th route for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) { HashMap<String, String> point = path.get(j); double lat = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lat")); double lng = Double.parseDouble(point.get("lng")); LatLng position = new LatLng(lat, lng); points.add(position); } // Adding all the points in the route to LineOptions lineOptions.addAll(points); lineOptions.width(10); lineOptions.color(Color.RED); Log.d("onPostExecute","onPostExecute lineoptions decoded"); } // Drawing polyline in the Google Map for the i-th route if(lineOptions != null) { mMap.addPolyline(lineOptions); } else { Log.d("onPostExecute","without Polylines drawn"); } }從結果中提取上述點並在谷歌地圖上繪製路線。 這裡 ArrayList 點用於存儲谷歌地圖上的緯度和經度位置。
最後使用polyLine在Google Map上繪製路線: lineOptions.addAll(points);
添加折線到地圖,如: mMap.addPolyline(lineOptions);
最後運行應用程序。 它將成功運行。 屏幕的輸出如下所示。